Perfume bottles play a critical role in brand presentation, and when they malfunction, it can impact both product quality and customer satisfaction.PVC
A perfume bottle may fail to spray due to common issues such as a clogged nozzle or insufficient internal pressure, often caused by dried fragrance residues or air pockets. these technical aspects enables brands to quickly diagnose and resolve the problem, ensuring consistent performance and user satisfaction.
In fragrance packaging, the spray mechanism is complex, and small issues can cause significant disruptions. Commonly, blockages from dried perfume residue are major culprits. For fragrance brands, grasping these details is crucial to maintaining product performance.
Clogged nozzles are a primary reason for spray failure.Vero
Dried fragrance residues often block nozzles, preventing proper atomization and causing spray issues.
All perfume nozzles are designed to spray effectively.Falso
Different designs and materials can impact performance, leading to inconsistent spray results.
Why Do Perfume Bottles Fail to Spray?
Dried perfume residue that can cause spray mechanism blockages includes alcohol crystals, thickened essential oils, coloring agents, sticky fragrance fixatives, and water, all of which can lead to buildup and clogs.
Dried perfume residue consists of precipitated alcohol crystals, viscous essential oil compounds, coloring agents that may settle, adhesive fragrance fixatives, and residual water content.
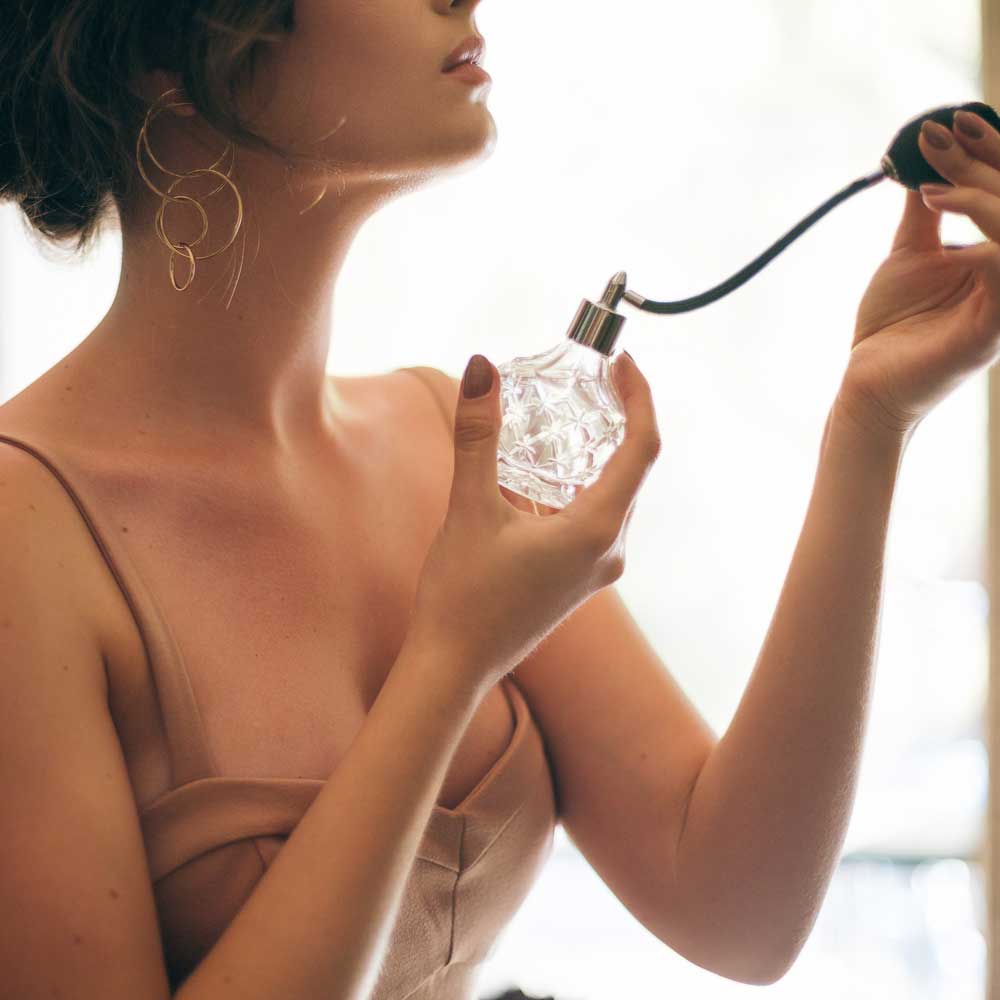

A clogged nozzle can be a major reason for spray failure, often caused by dried residue or dirt. However, issues may also arise from design flaws or low-quality components, making it essential to address these concerns promptly.
Anti-clog nozzles effectively minimize spray interruptions.Vero
Innovative anti-clog technology helps reduce blockages by preventing residue accumulation in the nozzle.
Standard nozzles work well for all liquid types.Falso
Different liquids need specific nozzles designed to accommodate various viscosities, pressures, and chemical properties.
Which Spraying Systems’ Devices Minimize Clogging?
The most advanced anti-clogging technologies for sprayers today include a variety of innovative methods. Leading the way is ultrasonic atomization technology.
Ultrasonic atomization technology uses ultrasonic vibration to break down liquid into fine particles, completely avoiding the clogging of traditional nozzles. This technology is widely used in high-end perfume and medical sprayers and has become a leading solution
What Types of Liquids Can a Nozzle Spray?
Ultrasonic atomization technology prevents clogging by using high-frequency vibrations to create ultra-fine particles. This ensures a consistent mist and precise application, making it popular in high-end perfume and medical sprayers. As industries seek efficient solutions, this method sets a new standard for performance and user satisfaction.
Water-Based Liquids
Water-based liquids include pure water and diluted solutions, making them ideal for applications like agricultural spraying, cleaning, and humidification. These liquids are easy to atomize and often require minimal adjustment to standard nozzle designs.
Oil-Based Liquids
Oil-based liquids, such as lubricants, essential oils, and perfumes, require specially designed nozzles to handle their viscosity and ensure an even spray. Nozzles for these liquids are often customized to achieve a fine mist while managing thicker fluid properties.
Chemical Solutions
Chemical solutions, including pesticides, disinfectants, and cleaners, demand corrosion-resistant nozzle materials to withstand the effects of chemical exposure. These nozzles ensure safety and longevity when handling reactive substances.
Viscous Liquids
Viscous liquids, such as emulsions and gels commonly used in cosmetics and food industries, often need pressurized spraying or larger nozzle diameters. These adaptations help achieve a consistent spray pattern even with thicker substances.

Fuel-Based Liquids
| Liquid Type | Description | Nozzle Requirements | Application Scenarios |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water-Based Liquids | pure water and diluted solutions | Standard nozzles, typically no special adjustments needed. | Agricultural spraying, household cleaning, humidification |
| Oil-Based Liquids | lubricants, essential oils, and perfumes | Specially designed to handle viscosity and ensure an even spray | Perfume spray, lubricant applications, aromatherapy |
| Chemical Solutions | Includes pesticides, disinfectants, and cleaners. | Corrosion-resistant materials to withstand chemical exposure | Pesticide spraying, disinfecting, industrial cleaning |
| Viscous Liquids | Such as emulsions and gels, used in cosmetics and food industries | Requires pressurized spraying or larger-diameter nozzles | Cosmetic spraying, food additive spraying |
| Fuel-Based Liquids | Such as diesel and gasoline, used in engines and combustion systems. | Heat-resistant nozzles with precise spray control | Engine fuel injection, combustion equipment |

Nozzle testing reduces product failure rates and enhances reliability.Vero
By identifying potential issues early, nozzle testing ensures stable performance, minimizing rework and customer complaints.
All nozzles perform the same regardless of liquid type.Falso
Nozzle performance varies based on liquid viscosity, pressure requirements, and material compatibility, making specialized nozzles essential for different applications.
How to Perform Quality Control on Nozzles?
Visual Inspection
Check for any visible defects, such as cracks, uneven surfaces, or blockages.
Ensure that all components are intact and properly aligned.
Spray Pattern Consistency 1
Test the nozzle with the intended liquid and observe the spray pattern.
Ensure that the nozzle produces a consistent, fine mist without dripping or sputtering.
Use pattern testers to verify that the spray coverage matches specifications.
Flow Rate Testing
Measure the flow rate to confirm it aligns with product requirements.
Check that the flow remains steady over multiple uses.
Clog Resistance Testing
Conduct clog-resistance tests by spraying various liquids, including thicker and essential oil-based solutions.
Evaluate nozzle durability by testing it over extended use to ensure it resists residue buildup.

Pressure Tolerance Testing
Apply different levels of pressure to ensure the nozzle can handle the maximum pressure without leaking or damage.
This test is particularly important for pressurized systems or viscous liquids.
Corrosion and Material Testing
For nozzles handling chemical solutions, test the nozzle materials for corrosion resistance.
Perform endurance tests by exposing the nozzle to chemicals over a prolonged period.
Heat Resistance 2 (for Specific Applications)
For fuel-based or high-temperature applications, test nozzles for heat tolerance to ensure material stability.
Assess whether the nozzle maintains spray consistency under high temperatures.
Assembly and Fit Testing
Confirm that nozzles fit 3securely with their corresponding bottles or dispensing systems.
Check for any leaks at the connection points, ensuring a tight, reliable fit.
Nozzle testing ensures product quality stability, reduces rework and maintenance costs, enhances customer satisfaction, and strengthens brand credibility.
What are the international testing standards for nozzles?
| Parameter | Requirement/Range | Reference Standard | Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Flow Rate Accuracy | ±5% (Agricultural), ±1% (Industrial) | ISO 5682-1, ASTM D4212 | ±5% for agriculture; ±1% for labs. |
| Spray Angle | ±3° | ISO 10625 | Common angles: 80°, 90°, 110°. |
| Droplet Size Distribution | 150-300μm (Agriculture), <100μm (Fine Spray) | ISO 25358 | 150-300μm for farms; <100μm for fine mists. |
| Corrosion Resistance | 48-hour salt spray test | ISO 9227 | 48 hours for agriculture; 100+ hours for chemicals. |
| Operating Pressure Range | 1-10 bar (Standard), 20+ bar (High-Pressure) | ANSI/ASABE S572.1 | 2-4 bar for agriculture; 20+ bar for industrial use. |
| Uniformity of Spray Pattern | CV < 10% | ISO 5682-1 | CV under 10% for even coverage. |
| Heat Resistance | 100°C (Standard), 200°C+ (High-Temp) | ASTM D2240 | 200°C for industrial; 250°C for fuel use. |
Regular quality control is essential for nozzle performance.Vero
Implementing consistent testing and inspections ensures that nozzles meet required standards and function properly.
Visual inspections alone are sufficient for quality control.Falso
Comprehensive quality control requires functional testing in addition to visual inspections to identify performance issues.
Conclusione
Understanding and selecting the appropriate spray nozzle technology can significantly impact product performance , efficiency, and customer satisfaction. Careful selection tailored to liquid type, viscosity, and intended use ensures the best results for each application.
-
Learn about spray pattern uniformity and its importance in agriculture.: Uniform spray distribution is key for maximizing coverage and effectiveness in agricultural applications, enhancing crop yield. ↩
-
Understand the role of heat-resistant nozzles in fuel and high-temperature applications.: Heat-resistant materials prevent deformation and ensure safe, reliable performance in combustion systems and fuel injection. ↩
-
Discover how nozzle materials affect environmental sustainability.: Choosing eco-friendly and durable materials in nozzle production reduces waste and supports sustainable practices. ↩